When it comes to solving sequence-related tasks in machine learning, Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) remain a core technology. They’re particularly useful in applications involving time-series data, natural language processing (NLP), and audio processing. Among the variants of RNNs, Gated Recurrent Units (GRUs) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTMs) are the most commonly used.
LSTMs and GRUs are both meant to fix problems with regular RNNs, especially the disappearing gradient problem, but they don't always work together. Each has its qualities that make it better for certain jobs. This post breaks down the differences between GRUs and LSTMs and explains when and why GRUs should be chosen over LSTMs. The aim is to help data scientists and AI developers make more efficient model architecture decisions without diving into overly complex theories.
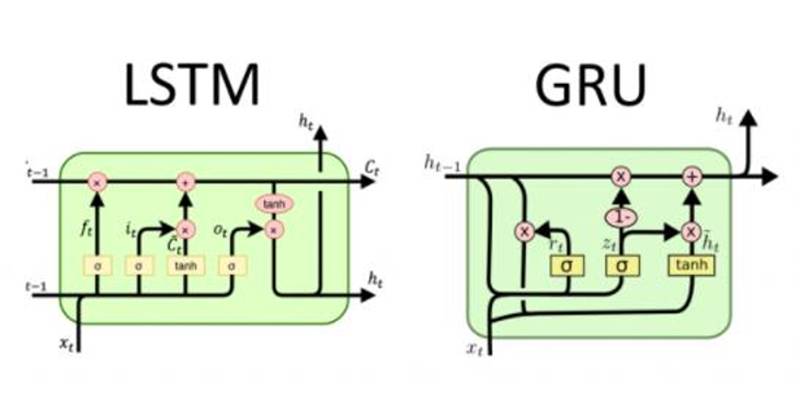
LSTM Architecture: Memory with Fine Control
The LSTM architecture was introduced in 1997 as a solution to the problem of vanishing gradients that plagued traditional RNNs. LSTMs are designed to capture long-range dependencies in sequence data, which makes them especially powerful for tasks where the model needs to remember information over long sequences.
The LSTM's key feature is its memory cell, which can maintain information for extended periods. Three types of gates control this memory cell:
- Forget Gate: Decides what information to discard from the memory cell.
- Input Gate: Determines which values will be updated in the memory cell.
- Output Gate: Controls what part of the memory cell is output.
This architecture allows LSTMs to have fine control over the flow of information and enables them to remember or forget specific data based on the task at hand. This level of control makes LSTMs highly effective for complex sequence tasks where long-term dependencies are crucial.
GRU Architecture: Elegant Simplicity
Introduced in 2014, the GRU simplifies the LSTM model without sacrificing too much performance. The GRU uses only two gates instead of three, which reduces the complexity of the model:
- Reset Gate: Decides how much of the previous memory to forget.
- Update Gate: Controls how much of the new information should be stored and how much should be carried forward.
By removing the forget gate and simplifying the memory cell, GRUs make the model computationally lighter and easier to train. Despite their simplicity, GRUs still tackle the vanishing gradient problem effectively, making them a competitive alternative to LSTMs, especially in tasks that don't require extensive memory control.
When to Choose GRUs Over LSTMs?
Choosing between GRUs and LSTMs is often a matter of context. Both architectures have their strengths and weaknesses, and the right choice largely depends on the specifics of your project. Let’s break down when GRUs might be the better option.
Computational Efficiency: GRUs Win
If computational resources constrain your project or you are working on a real-time application, GRUs are often the better choice. Due to their simpler architecture, GRUs typically train 20-30% faster than LSTMs. For example, during a recent experiment on consumer review text classification, a GRU model took 2.4 hours to train, while an equivalent LSTM model took 3.2 hours.
The reduced computational burden makes GRUs ideal for real-time applications, mobile or edge computing, and environments with limited hardware. If you need faster inference times, GRUs will often outperform LSTMs without compromising accuracy significantly.
Shorter Sequences: GRUs Excel
When dealing with relatively short sequences, such as text inputs with fewer than 100 tokens or time series data with limited past dependencies, GRUs generally perform just as well as LSTMs while requiring less computational effort. It is because GRUs have a more straightforward architecture that’s well-suited to capturing the relevant patterns without the complexity of maintaining a separate memory cell, as is done in LSTMs.
If you're working with tasks like basic sentiment analysis or simple classification of short sequences, GRUs are a fantastic choice due to their simplicity and efficiency.
Smaller Datasets: GRUs Have the Advantage
If you are working with a smaller dataset, GRUs can be advantageous over LSTMs. Because GRUs have fewer parameters and require less training data to reach convergence, they are less likely to overfit when compared to LSTMs, especially in cases where the dataset is small.
In my experience, GRUs often converge more quickly and with fewer epochs than LSTMs. It can be especially beneficial when the amount of data is limited, as the model can learn faster and generalize better.
Faster Prototyping: GRUs for Quick Iterations
When you’re in the early stages of a project and need to quickly experiment with different architectures, GRUs provide a faster iteration cycle compared to LSTMs. Since they train more quickly and converge faster, you can test hypotheses and explore different configurations in less time. It is particularly useful in rapid prototyping scenarios, where time is of the essence.
Practical Decision Framework

When deciding between GRUs and LSTMs, consider the following key questions:
- Resource Constraints: Are you limited by computation, memory, or deployment requirements?
- Yes → Consider GRUs
- No → Either architecture may work
- Sequence Length: How long are your input sequences?
- Short to medium sequences (< 100 steps) → GRUs often suffice
- Long sequences (> 100 steps) → LSTMs may perform better
- Dataset Size: How much training data do you have?
- Limited data → GRUs might generalize better.
- Abundant data → Both architectures can work well
- Experimentation Budget: How much time do you have for model development?
- Limited time → Start with GRUs for faster iteration
- Ample time → Test both architectures
Conclusion
Choosing between LSTMs and GRUs can be challenging, but it ultimately depends on the specific needs of your project. If you are constrained by resources, working with moderate-length sequences, or need faster convergence, GRUs are an excellent choice. However, if your task involves handling very long sequences with complex dependencies, LSTMs might be the better option. Remember, the choice of architecture is not the only factor that impacts performance. Feature engineering, data preprocessing, and regularization also play significant roles in determining the success of your model.











